
Single Node Loop of an Electron
THE NATURE OF MATTER
PHYSICS
MYSTERIES
EXPLAINED
THE ROTATION OF ENERGY
CHAPTER 9
SINGLE NODE ENERGY ROTATION
ENERGY ROTATION IN ELECTRONS
ENERGY ROTATION IN DOUBLET COMPOUNDS
THE ROTATION OF ENERGY
The deduction of the Unit Particle of Matter
Substructure Theory, and the subsequent distinction between matter and energy
as components of Standard Model particles provides a physical cause for the mathematics
of the quantum wave function of a given particle, which is that the math describes
the motion of the energy within the particle structure.
The wave function of a particle is a mathematical description of the rotation of
energy bound within the particle structure.
The deduction of the Unit Particle of Matter
Substructure Theory, and the associated distinction between matter and energy
as components of Standard Model particles, elucidated a pattern that energy is at
all times is hosted by a unit particle of matter. It is proposed that energy must
at all times be hosted by a unit particle of matter.
The quantum wave function of a particle is fundamentally a description of the motion
of energy bound within the unit particle of matter substructure of the particle.
Single node energy rotation is defined as a rotation that which equals one half
of the wave length of the wave function.
Single node energy rotation requires that the energy make two 360 degree rotations
to be in the same phase as at the start of the rotation because one 360 degree rotation
only equals a 180 degree phase shift in the wave function.

Single Node Loop of an Electron
Single node energy rotation requires that the energy make two 360 degree phase rotations
to be in the same phase as at the start of the rotation because one rotation is only
half the wavelength. After one 360 degree rotation of energy, the wave function is
180 degrees out of phase compared to the start of the rotation.
The following plots give an idea of what it might look like if energy in Kepler rotation
was a wave of energy. Since energy is known to be organized in quanta, it is not
unreasonable to consider the possibility that the wave packet might be composed of
a given number of individual energy particles bound to a common center of matter
with the motion of each energy particle making the wave. In the case of a great number
of individual energy particles making the wave packet, it is easy to visualize from
the plots how the wave packet would disperse and revive as individual energy particles
came into or out of phase.

The Picture Book of Quantum Mechanics
Second Edition by Siegmund Brandt and Hans Dieter Dahmen
published 1994 by Springer-Verlag
The above plots of the fractional revival of a wave packet are from The Picture Book of Quantum Mechanics by Siegmund Brandt and Hans Dieter Dahmen published in 1994 by Springer-Verlag. The plot are of the quantum mechanical probability density in the Kepler plane for various fractions of the revival time.

The plots above of a three dimensional wave packet are plots of the fundamental
harmonic, and the first and second harmonics.
If you imagine the higher harmonics superimposed on the fundamental, then you can
imagine a more realistic picture of quantum mechanical energy rotation within a particle
structure.
Energy rotation for electrons works like this:
after 1 rotation the phase of the energy is 180 degrees out of phase from the start
after 2 rotations the phase of the energy is 360 degrees out of phase from the start
- or back in phase
The evidence that rest mass is a closed loop is precisely that the loops only occur at harmonic intervals, as in the electron. The harmonic intervals of resonance manifest feedback, which is a property of a closed loop.
Quantum Angular Momentum
Quantum angular momentum is not analogous to rotation of a solid body such
as a planet. The rotation of energy around an electron through 360 degrees does not
return the electron back to the same phase as at the start of the rotation, as it
takes another 360 degree rotation to return the electron to the same phase as when
the rotation started.
Speculation on Electron Internal Structure
Electron = ![]() (a negative unit of matter) + .51 MeV = negative unit matter host + .51 MeV of structural
energy
(a negative unit of matter) + .51 MeV = negative unit matter host + .51 MeV of structural
energy
The electron energy could be speculated to be in several forms within the electron.
1. The energy units could be bound directly to the electron singlet host.
2. The energy units could be bound as photon of energy which are then bound to the singlet host.
The energy units well could be unit photons with the energy bound on a doublet
structure, however, the electron has its energy bound to a singlet unit particle
of matter. Therefore, the electron is the first structure made with a singlet substructure,
and it takes energy which is actually bound first to doublets in the form of unit
photons, and then in a secondary way, the unit photons are bound around the singlet
unit particle forming the electron substructure.
The energy of the electron is bound in secondary rotation around the singlet unit
particle forming the electron substructure, as opposed to the direct bind of the
energy to the doublets of the unit photons within the electron.
Non-Locality of Energy in the Electron
When the energy units travel in rotation about a host unit particle (which
is described by the wave function) a channel or force free path can be postulated
to be cleared in the closed path. Within the cleared path, the location of the energy
units is given by the probability of the wave function. The key point is that due
to non-locality within the wave function, we can be sure that the energy units within
the wave function are non-local. Non-local implies either magic or verymuch faster
than light speed unit energy particles carving the wave function which are as a bundle
are so fast as to be called non-local.
A force free path means possibly that the background is removed from the path
allowing energy to travel freely. This would mean that magnetic flux is not involved
in the energy location within the wave packet, therefore the location of the energy
within the wave packet is not electromagnetic.
The path that the energy units have cleared is the electrical field. To electrical
field is the expression of energy bound to a host unit charge unit particle of matter.
Suppose within the electric field lines of force that the background oceanic particles
have been cleared and that the energy units do not have the restriction of moving
at the speed of light because there is no interaction with the oceanic particles,
no magnetic flux.
No interaction with the oceanic particles also necessarily means that the energy
units do not have mass because Higgs field, or background ocean, is what causes mass,
and if the oceanic particles are cleared from the path, then the energy does not
exhibit mass. In other words, with no background ocean in the free path to slow the
energy units down to the speed of light, the energy can travel much faster than the
speed of light, and be non-local.
The energy units traveling in a background free path do not have mass as there is
no background there, therefore no electromagnetic interaction.
Rest mass is a closed loop of energy, a constant amount of energy bound to the particle
structure.
The phase of an electron in its wave function is caused by the energy in rotation
around the host charge unit particle of matter.
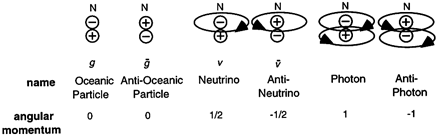
ENERGY ROTATION IN DOUBLET COMPOUNDS
The massless energyless background oceanic doublet particles may be viewed as
the basic form of matter, the source of matter. The background oceanic particles
have no energy bound in rotation around their doublet substructure as the background
oceanic particles have neither rest mass nor momentum.
The electron neutrino was deduced in The
Steps of Deduction Step 2 to be a massless doublet possessing momentum energy
with the energy bound in a way such that it is in rotation in only one direction.
It is proposed that the reason the energy of a electron neutrino is in rotation about
the particle structure in one direction is because of the way the weak force impart
energy onto the doublet substructure.
A photon were deduced to have a doublet unit particle of matter substructure with
two sets of energy bound in rotation in two directions about the substructure of
the photon. Chapter 8 Photons discusses photons and
their electric and magnetic field alignments.
Think you understand the Unit Matter Substructure
Theory?
Think you understand the Background of Matter Theory?
Comments welcome: jrees@starlight-pub.com
Last Update April 23, 2000
Copyright © 2000 Starlight Publishing Company Hermosa Beach, CA